EWASH trial comparing hypochlorous acid to bleach

Sector:
healthcareRegion:
nigeriaProduct:
salvesanThis trial was conducted by Dr Giorgia Gon from the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine and funded by the WHO comparing hypochlorous acid to bleach for infection control in Nigerian hospitals.
Bleach was used at a concentration of 500ppm with the hypochlorous acid/electrolysed water (EW) at a concentration of 150ppm.
BACKGROUND
- Environmental hygiene is a key aspect of IPC in hospital settings.
- Cleaning practices in hospitals in low-income countries continue to rely on sodium hypochlorite
(“bleach”), which is corrosive, toxic and requires accurate dilution. - Neutral Electrolysed Water (EW) is an innovative surface disinfectant with high-level antimicrobial activity which is neither toxic nor corrosive, and presents no environmental hazard.
METHODOLOGY
- A non-inferiority, multi-period, cross-over cluster randomised trial was used to evaluate the efficacy of EW for surface disinfection compared to standard disinfectant (chlorine-based bleach) in two hospitals in Abuja, Nigeria, over six weeks in 2021.
- Clusters were the female (medical and surgical), male (medical and surgical),and labour wards in each hospital
- Three clusters were selected in each hospital and randomly allocated to one of the two intervention control sequences.
- The allocation was created by the study statistician.
- Each week, the cluster received the allocated product for 4 days and there was a wash-out period of 3 consecutive days during which standard cleaning products were used.
- Hospital staff and data collectors were blinded to the treatment allocation because the products were provided daily with identical bottles and prepared by the project manager.
- Microbiological cleanliness was measured using double sided dipslides with non-selective agar for Aerobic Colony Count (<2.5 cfu/cm2 = clean; ≥2.5 cfu/cm2 = not clean).
RESULTS
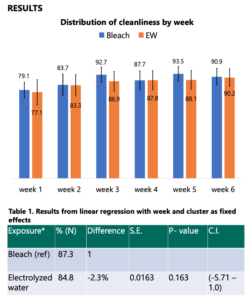
CONCLUSIONS OF COMPARING HYPOCHLOROUS ACID TO BLEACH
- This was the first randomised trial to assess the efficacy of EW compared to bleach for hospital disinfection in LMICs. Our findings suggest that EW performs similarly to bleach.
- EW performs similarly to bleach at a lower concentration.
- We estimate that EW is ~10 times cheaper when produced locally compared to currently procured bleach
- EW is less corrosive for cleaners’ skin and materials
- EW’s environmental residue is negligible compared to bleach
- EW can be used for a wide set of applications: e.g. wound burns, medical equipment disinfection.
To see the full EWASH Poster click here.
To read the case study on fogging HOCl in the NHS click here.

